
2022-2023 CHAIR’S INITIATIVE
Strengthening Youth Mental Health
The United States faces a nationwide youth mental health crisis. The roots of this crisis existed before COVID-19, but the pandemic has both exacerbated and highlighted the scope of the challenges in addressing this issue. The time is right and the need has never been more apparent to discuss proven and innovative solutions for states.
Strengthening Youth Mental Health: A Governor’s Playbook

Even before the pandemic turned the world upside down, our young people were struggling with a mental health crisis that has only grown more serious in recent years. Yet we have reason to feel optimistic that we can reverse these trends and help our children.
Over the past year, we have spent countless hours meeting with those on the front lines of this crisis, and we have seen innovative approaches, thoughtful programs, and effective models across the country. Together, they form the basis of this playbook that states, policymakers, and stakeholders can use to address youth mental health challenges.
These are issues that impact every community – urban, suburban, and rural, east, west, north, and south. There are no geographic boundaries or political party lines. As Governors, one of our most important and sacred responsibilities is protecting the health and well-being of our state’s children. Mental health is just as important as physical health, and while many are unfamiliar with the signs and symptoms of mental illness, we’re encouraged by the extensive efforts taking place across the country to raise awareness and reduce stigma. As more and more people know it’s okay to say they’re not okay, we know we’re seeing significant progress.
But this crisis is too deep and complex for any state or organization to solve on its own. It requires partnership from everyone, especially the folks on-the-ground in our communities – young people, parents, caregivers, educators as well as business, community, and faith-based leaders to work together. The pages of this playbook contain examples of successful policies and initiatives that use this all-hands approach to address youth mental health needs, and it is our hope that more states will implement similar policies.
We want to extend our deepest thanks to everyone who shared their expertise in helping to create this playbook. We are especially grateful to those who shared their lived experience. Throughout my year as Chair, this Initiative has honored the need to listen to youth voices and perspectives to collaboratively find more effective ways to meet the mental health needs of our youth.
Our kids deserve better, and we can do better. It will not be easy, but this playbook offers a path to ensuring young people can get the help they need when they need it. Together, we can help our youth and our communities heal.
— New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy, NGA Chair
If you or someone you know is having thoughts of suicide or experiencing a mental health or substance use crisis, 988 provides 24/7 connection to confidential support. There is Hope. Just call or text 988 or chat 988lifeline.org
Executive Summary
Across the country, on social media, in pop culture, around kitchen tables and in state capitols, the focus on youth mental health has become increasingly common. Governors and policymakers at all levels of government and on both sides of the aisle are continuing to seek to make positive impacts on youth mental well-being and the systems that support young people. As Chair of the National Governors Association (NGA), New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy sought to harness the bipartisan efforts and national focus on youth mental health and made Strengthening Youth Mental Health the focus of his year-long NGA Chair’s Initiative. The Strengthening Youth Mental Health Initiative brought together close to 500 people, including youth, Governors and other experts, in four convenings held across the country to discuss the current state of youth mental health systems and advance best practices and implementable, impactful solutions for states. Strengthening Youth Mental Health: A Governor’s Playbook is a culmination of those discussions as well as more than 50 learning calls with national experts.
The Playbook is intended to serve as a tool for states to further impactful policy solutions that strengthen youth mental health. Nationally, the current state of youth mental health is often labeled as a crisis – youth have not been provided the tools and resources they need to thrive, young people often do not know where to go to begin to understand their mental health needs and they face a mental health care system that is often inaccessible and unaffordable when they do need it. Young people are not alone in their efforts to support their own mental and emotional health. Parents, caregivers, educators, peers and other youth-facing adults want to support the mental well-being of the youth in their lives but face similar barriers to understanding what they need and how to help them. The Playbook provides states with actionable solutions to address each of these concerns.
The Strengthening Youth Mental Health Initiative consists of four pillars that address the core challenges to a system that supports youth and helps their mental well-being. Altogether, the four pillars address the continuum of youth mental health, helping states to address the needs of youth in crisis today, while ensuring that systems focus on holistically supporting youth mental well-being to help future generations succeed. The four pillars are:
- Addressing prevention and building resilience: Supporting youth with the necessary tools to respond to stressors and challenges, reducing the risk of mental health conditions, and proactively identifying and managing existing conditions to prevent crises.
- Increasing awareness and reducing stigma: Promoting awareness of mental health knowledge and resources, and decreasing the social, self and structural stigma around youth mental health challenges.
- Ensuring access and affordability of quality treatment and care: Removing the barriers to care, including unaffordable costs, lack of insurance coverage and a depleted workforce to ensure that high-quality, trauma-informed and culturally relevant care is accessible to youth in appropriate places, spaces and timeframes to meet their needs.
- Training and supporting caregivers and educators: Expanding training and supports so that those caring for and interacting with youth daily have the understanding and tools to identify mental health needs to access relevant supports.
The opportunities noted in the Playbook are not exhaustive of all potential actions that Governors can take to address youth mental health in their states, but are instead a representative collection of replicable, implementable and impactful solutions that are already underway across the country. The ultimate goal of the Playbook is to help Governors understand the best practices and ideal status of youth mental health systems and then to provide examples and context for how to adapt and implement them in their states.
Further, the Playbook recognizes there is a vast diversity of youth identities and experiences that interact with mental health outcomes in unique ways. The Strengthening Youth Mental Health Initiative deliberately does not define an age range or limit the focus of policy opportunities to specific types of youth to empower Governors to determine the target audiences for the mental health programs in their states across their unique backgrounds, experiences and stages of life.
Finally, while the Playbook can be utilized as a standalone resource, it is not the only support available to states in conjunction with this effort. The Playbook represents the culmination of Governor Murphy’s Chair’s Initiative, but the Strengthening Youth Mental Health effort will continue on beyond his time as NGA Chair. In addition to the representative sampling of state efforts included in the Playbook, a more comprehensive database of Governor’s collective efforts can be found at: www.nga.org/youthmentalhealth. The NGA and Strengthening Youth Mental Health partners also remain accessible for technical assistance for implementation of the Playbook’s recommendations as well as guidance on additional efforts Governors can pursue to Strengthen Youth Mental Health in their states across the country.
Introduction
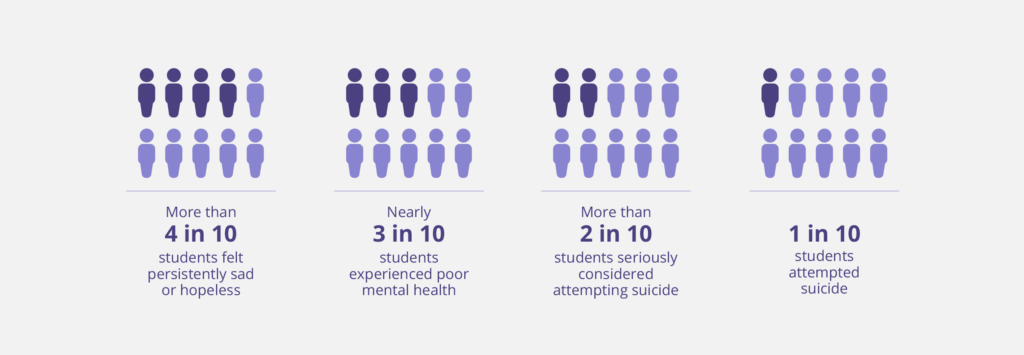
The United States has a widely recognized youth mental health crisis. Data released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show the continuation of a 10-year rise in young people’s mental health challenges. In 2021, more than 40% of students felt persistently sad or hopeless, and for teenage girls, this number was nearly 60%. More than 20% of all students and nearly 50% of LGBTQ+ students seriously considered attempting suicide. The CDC also reports an increase in suicide rates among younger Americans in 2021, with a 37% increase in the suicide rate for Black youth aged 10 to 24. American Indian or Alaska Native youth continued to have the highest suicide rates for youth aged 10 to 24 at 36.3 deaths per 100,000 persons in 2021.
However, the crisis does not need to go unsolved. While historically mental health support, including innovative treatment and dedicated funding, has been targeted towards adults, addressing youth mental health and well-being is increasingly front and center for states. In 2022, more than 30 Governors highlighted mental health as a major priority in their State of the State or Budget Addresses. Recognizing rising youth mental health needs and the unique position of Governors to advance solutions, as Chair of the National Governor’s Association, New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy selected Strengthening Youth Mental Health as the 2022-2023 NGA Chair’s Initiative for cross-state engagement and collaboration on relevant solutions. The Chair’s Initiative brings together Governors, their advisors, youth voices and leaders across the public and private sectors to advance impactful programs, policies and partnerships that can be tailored to state-specific contexts.
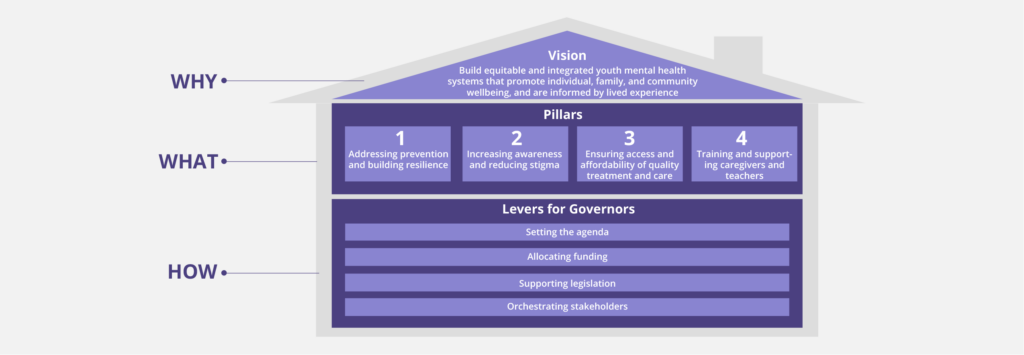
The vision for Strengthening Youth Mental Health is to build equitable and integrated youth mental health systems that promote individual, family and community well-being, and are informed by lived experience. Achieving this vision is enabled through four pillars, with distinct but interconnected themes:
- Addressing prevention and building resilience: Supporting youth with the necessary tools to respond to stressors and challenges, reducing the risk of mental health conditions, and proactively identifying and managing existing conditions to prevent crises.
- Increasing awareness and reducing stigma: Promoting awareness of mental health knowledge and resources, and decreasing the social, self and structural stigma around youth mental health challenges.
- Ensuring access and affordability of quality treatment and care: Removing the barriers to care, including unaffordable costs, lack of insurance coverage and a depleted workforce to ensure that high-quality, trauma-informed and culturally relevant care is accessible to youth in appropriate places, spaces and timeframes to meet their needs.
- Training and supporting caregivers and educators: Expanding training and supports so that those caring for and interacting with youth daily have the understanding and tools to identify mental health needs to access relevant supports.
Progress in each of these pillars is supported by key levers Governors and other state leaders can use to drive change:
- Setting the agenda: Clearly identifying priorities, empowering state agencies to act, and endorsing relevant organizations and their initiatives to set the “tone from the top.”
- Allocating funding: Appropriating sufficient funds to youth mental health, leveraging federal funding sources effectively and exploring innovative funding approaches with private sector organizations and philanthropies.
- Supporting legislation: Directing legislative platforms towards key issues, introducing supportive legislative proposals and advancing relevant policies.
- Orchestrating stakeholders: Employing strategies including cross-sector coalition building and working groups, allocating responsibilities to stakeholders and identifying leaders to drive alignment throughout state systems to better coordinate resources across disparate structures.
Historically, agencies that cover public health or child welfare have often been the primary drivers of statewide youth mental health agendas. However, impactful solutions to strengthen youth mental health often require a systems approach and benefit from cross-agency coordination and leadership, including but not limited to education, insurance regulators, social safety net programs, workforce boards, juvenile justice systems, human services and Medicaid agencies, many of which were not developed and designed to address the unique and specific needs of youth. Families often interact with multiple systems in a state, and coordination between these systems can be critical to getting families the help they need. A successful youth mental health agenda often starts with building momentum out of youth-facing state systems. Governors can champion and commit to a unified statewide strategy, compel agencies to come together to solve problems, braid and blend funding, remove administrative barriers and share information with the goal of improving family well-being.
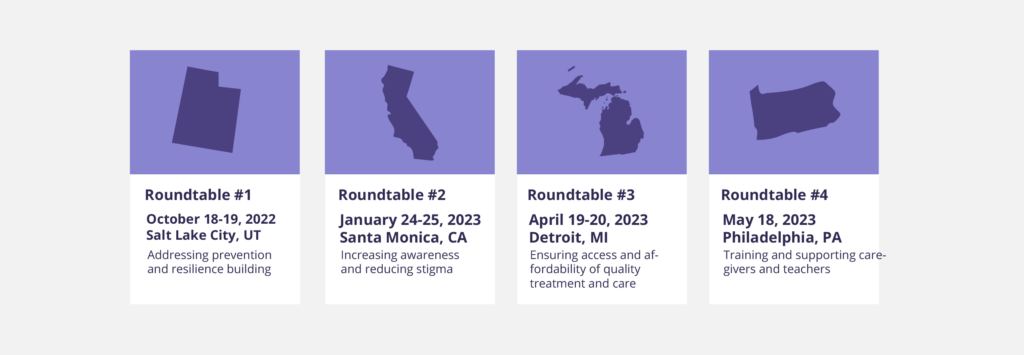
The 2022-2023 NGA Chair’s Initiative held four roundtable discussions – one per pillar – across the country, from October 2022 to May 2023. Across the four roundtables, more than 14 state representatives were joined by over 400 community leaders, academic experts and representatives from partner organizations and funders. In total, more than 60 organizations were represented throughout the Initiative. The key takeaways from these discussions were supported through over 50 learning calls with other relevant organizations and individuals and an in-depth landscape analysis of states’ and territories’ activities to strengthen youth mental health.
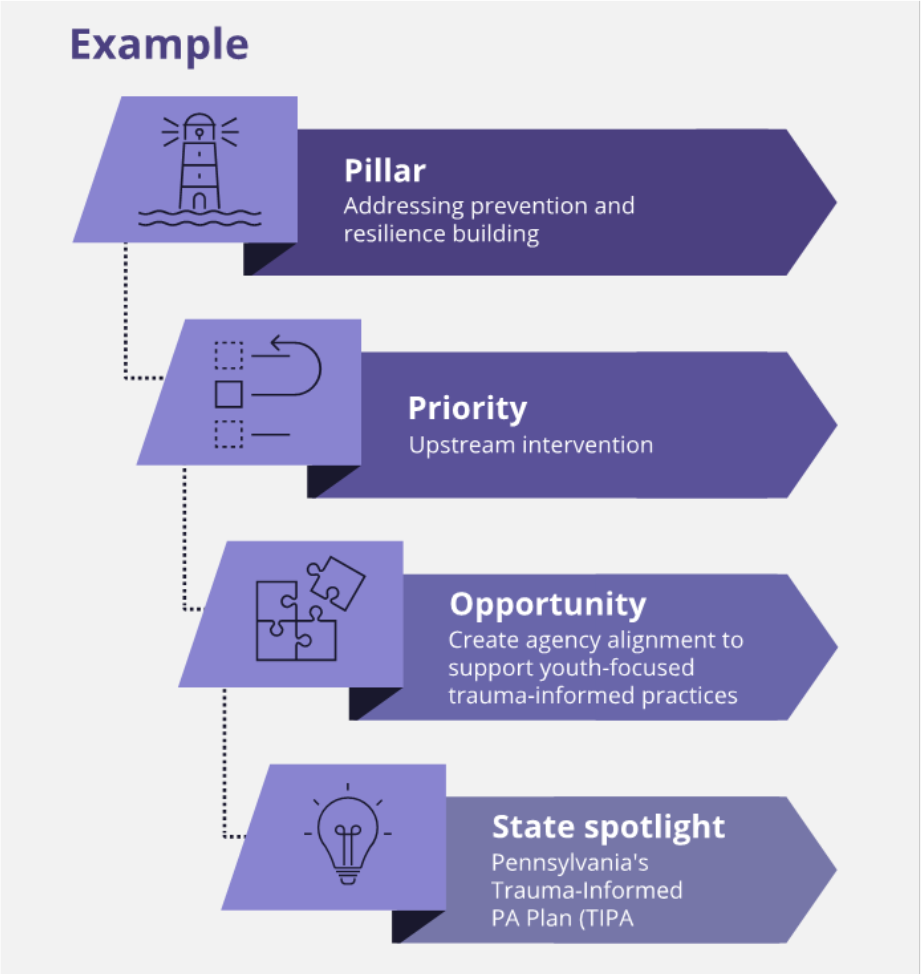
A Governor’s Playbook is the culmination of the 2022-2023 NGA Chair’s Initiative: Strengthening Youth Mental Health and focuses on actionable ways to improve youth mental health and ensure that resources, innovation and attention are directed towards children and youth. The publication is organized according to the four pillars of the initiative. Each pillar is supported by a set of priorities, or focus areas, which can be enabled through opportunities: specific action itemsfor Governors and state leaders and state spotlights to highlight states’ policies and programs.
The youth mental health landscape is complicated and nuanced and no solution can be representative of every child or youth’s unique experience. The Playbook recognizes the disparate outcomes experienced by youth of diverse identities, communities and environments, including youth of color, LGBTQ+ youth, multi-system youth, youth from families with low incomes and youth with co-occurring disorders, including substance use. The Playbook also covers solutions across all ages, from early relational health to transition-age programs. The National Governors Association supports Governors’ efforts to strengthen the mental health of all youth in their states, including youth across all backgrounds, experiences and stages of life.
Not all examples will be relevant for all states, due to differing priorities and populations, but A Governor’s Playbook aims to support state policymakers in navigating the youth mental health landscape and to inspire cross-state and cross-sector collaboration by amplifying the work already being done across the country. The examples selected for this Playbook highlight different responses to the youth mental health crisis and were selected to illustrate some of the innovative and impactful initiatives across a range of states and territories. These examples are not intended to be exhaustive; many states are doing incredible work in youth mental health. To learn about additional state programs and examples, please see the online resource below. The highlighted examples in this Playbook aim to prompt more discussion on ways to advance progress.
Pillar 1: Addressing Prevention and Building Resilience
The mental health and well-being of a young person is affected by a mix of biological, psychological and environmental circumstances. Due to the ways in which these often intersect, preventing mental health issues is complex; however, by focusing on building resilience in youth, we can increase their ability to maintain or return to mental well-being when faced with stress or adversity and reduce the likelihood of engaging in unhealthy or damaging behaviors. States can foster mental well-being and reduce the risk of mental health challenges by focusing upstream on the root causes of youth mental health issues, supporting early identification of mental health conditions through screening and strengthening response systems to prevent suicide and other crises.
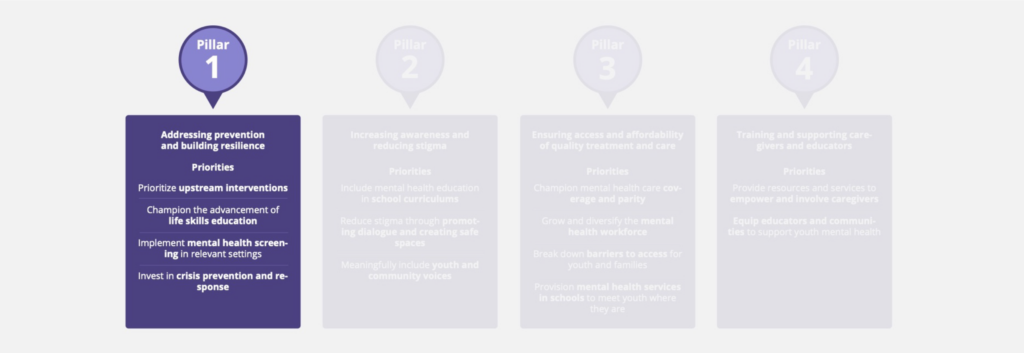
Priority: Prioritize upstream interventions
Prevention is better than cure. States have several opportunities to prevent mental or behavioral health conditions from developing or deteriorating, potentially avoiding harm to youth and strain on state services and resources. As Mental Health America notes, we are learning more about the “critical points in brain development and life experiences that increase the risk for or provide protection against the development of mental health disorders.” These critical points occur from infancy to adolescence and span across the different aspects of a young person’s life. To address youth mental health suitably, we need to start with early and holistic interventions.
Opportunity: Provide access to support services and early intervention for infant and early childhood mental health (IECMH)
Although significant focus is often on older children and adolescents, 16% of children aged two to eight years have a diagnosed mental, behavioral or developmental disorder, according the CDC. Many mental health challenges can be traced back to a child’s formative years. Mental health starts before birth, and investments that support IECMH often prevent the need for more costly interventions at a later age.
The majority of states are taking action on IECMH. Governors and state leaders can provide supports and resources to parents and caregivers, clinicians and child care providers looking for help to promote babies’ and toddler’s mental well-being or cope with mental health challenges. Prevention strategies for IECMH are only the beginning of supporting our youngest children’s mental well-being; states and territories can also incorporate IECMH practices into their Medicaid plans, allow for IECMH screenings in diverse settings and pay for quality family relational treatment. Several states have also expanded home visiting programs to connect mental health needs and promote well-being for both children and their caregivers. For example:
- In 2022, Colorado’s Department of Human Services launched an Early Childhood Mental Health Support Line to connect caregivers of children under age six with mental health resources.
- New Mexico’s Infant and Early Childhood Mental Health Services focuses on addressing the transmission of intergenerational trauma from parents to infants and shares resources including an infant mental health child parent psychotherapy provider directory.
- The U.S. Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting (MIECHV) Program supports 23 evidence-based home visiting programs in all 50 states, five territories and the District of Columbia. MIECHV programs in part support maternal mental health and the physical, social and emotional development of infants and young children from birth or during pregnancy, depending on the program. Oregon and New Jersey are the first two states in the nation to establish statewide universal home visiting programs that offer a nurse home visit to every family with a newborn at no cost to the family utilizing the Family Connects model.
- The U.S. Substance Use and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) also has a Center of Excellence for Infant and Early Childhood Mental Health Consultation that provides funding and technical assistance to community partners, states, territories and tribal partners.
- According to the National Center for Children in Poverty, more than 43 states use Medicaid to cover social-emotional screening of young children. More than 25 states allow for social-emotional screening to take place in some sort of a nonmedical setting, like in the home, within early intervention services, or within an early care and education program.
Opportunity: Address the social drivers of youth mental health issues
Social drivers of health, including income, access to education, health care, nutrition and safe housing, as well as repercussions related to discrimination and violence, are some of the leading causes of disparities in health and general well-being outcomes. Youth mental health challenges do not occur in a vacuum. According to the National Institute of Health, youth from homes with low socioeconomic status (SES) are twice as likely to suffer from mental health problems as those from homes with high SES.
State leaders can incorporate the needs young people have for healthy and thriving lives in their youth mental health efforts. Examples include:
- American Samoa, which has addressed income disparities through its Summer Youth Employment Program (SYEP) which offers work experience for economically disadvantaged applicants from ages 18 to 24.
- Hawai’i, which implemented the Safe Place initiative, a national youth outreach program designed to provide immediate emotional and physical support for homeless teens who are more likely to suffer from ACEs and worse mental health.
It is important to note that social drivers of health impact the experience and outcomes of youth across all systems. According to the 2019 National Academies The Promise of Adolescence report, children of color and of lower socioeconomic status experience lower rates of academic proficiency and higher rates of child welfare involvement, and such environmental factors can contribute to poor mental health outcomes. The report highlights potential factors that may contribute to disparities, including differences in family income, institutional response to adolescents by schools or the health system, or prejudicial or discriminatory attitudes or behavior on the part of adults in youth-facing systems. To address the social drivers of health comprehensively as a vehicle to prevent youth mental health concerns, Governors can drive progress in reducing these disparities holistically across all state systems.
Opportunity: Implement youth-focused trauma-informed practices
According to the CDC, over 60% of adults experience at least one adverse childhood experience (ACE) by age 18, including emotional, physical or sexual abuse; emotional or physical neglect; household challenges such as substance abuse or the incarceration of a family member; or environmental challenges such as discrimination. The number and severity of ACEs a child faces have a strong correlation to mental health issues. Governors and other state leaders can ensure training throughout youth-serving systems in trauma-informed practices to cater to youth who have experienced ACEs or toxic stress and can consider strategies to include families in their efforts to mitigate the occurrence of ACEs and improve family well-being. Further, states can promote positive childhood experiences, including community-building, to encourage strong social connections, a protective factor that contributes to mental and emotional well-being.

States have been advancing these efforts in unique ways. For example, Puerto Rico has prioritized training all clinical service providers on trauma-informed care practices and created four new regional Treatment Centers for Children and Youth to provide trauma-informed out-patient treatment for mental health and substance use to serve the four regions of the island. A powerful advocate for the reduction of ACEs, Oklahoma First Lady Sarah Stitt launched Hope Rising Oklahoma, a program that offers coaching and training for community-based organizations around building resilience, striving for well-being and fostering hope.
The NGA has supported state efforts on ACEs and trauma, including a multi-state technical assistance project on which it partnered with the National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP), culminating in State Actions to Prevent and Mitigate Adverse Childhood Experiences. Following this initiative, the State Trauma and Resilience Network (Connecticut, Delaware, Hawai‘i, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Wisconsin and Wyoming) was formed to share best-practices advancingstatewide, multi-agency and cross-sector efforts to address ACEs, trauma and resilience holistically in their states. Some examples from these states include Delaware, where Governor John Carney signed an executive order in 2018 to make Delaware a trauma-informed state, including training state employees on ACEs.In Pennsylvania, HEAL PA, a coalition of state agency representatives and community stakeholders, supported enactment of a bill requiring future legislation to consider childhood trauma.
Opportunity: Support the development of healthy school climates
The role of schools in youth mental health is not limited to what is taught in the classroom; schools should be a safe, supportive learning environment for all young people. Healthy school climates contribute to youth mental well-being by creating safe spaces for young people to share their feelings and ask for help from educators and/or their peers. As reflected in recent data from the Civil Rights Data Collection, youth of color are overrepresented in a number of data points; Black youth accounted for almost 40% of suspensions in schools but only 15% of public school enrollment. Youth struggling with their mental health or well-being can sometimes “act out” in schools, and ending disparities in suspensions, expulsions and incidences of bullying can help to promote supportive school environments.
An important first step can be understanding students’ experiences at school through data collection and analysis; for example, Colorado’s Healthy Kids Survey and Healthy Schools Smart Source is an annual survey of K through 12 students, to provide a more complete picture of youth and school health for over 70% of schools.
States can further support positive school climates and student success in different ways, such as:
- Wyoming’s Positive School Climate Grant, which provides school districts up to $9,000 to acquire and operate evidence-based programs to reduce school bullying and increase positive school culture and climate. Proposed outcomes must be quantified by using one metric and how that metric changed over time (e.g., discipline referrals, fights).
- Oklahoma’s State Department of Education, which released a Model Bullying Policy template to be used by school districts to develop anti-bullying policies in line with state statutes.
- To address the root causes of student behaviors, rather than approaches that are strictly punitive, Massachusetts requires schools to first use alternative forms of discipline, including behavioral health intervention, considering out-of-school suspensions a last resort.
Priority: Champion the advancement of life skills education
Youth face everyday stressors that can negatively impact their mental health if they do not have the necessary tools to manage them. One way to build resilience is through teaching life skills in schools and community programs. The definition of life skills can vary according to each state’s priorities, but traditionally comprises competencies such as self-regulation, problem-solving, interpersonal communication and adaptability that enable youth to navigate life’s challenges. According to the WHO Life Skills Education Schools Handbook, there is increasing evidence that learning life skills plays a vital role in the prevention and management of non-communicable diseases, including mental health conditions.
Opportunity: Support the development and implementation of school-based life skills curricula
According to Child Trends, in 2019, 31 states and territories had laws and regulations enabling life skills education to be taught in schools, with just under half mandating their inclusion. However, according to education publisher McGraw-Hill, only 22% of educators currently feel very prepared to teach life skills in classrooms, necessitating additional funding and professional learning opportunities for educators to implement teaching life skills in the classroom successfully.
States are addressing this in different ways:
- Arkansas’s G.U.I.D.E. for Life curriculum, based on the principles of Growth, Understanding, Interactions, Decisions and Empathy, was collaboratively developed by 96 educators across 74 schools and 44 districts.
- The implementation of Florida’s Resiliency Education Standards, adopted by the state Board of Education in 2023, is supported by $21 million in dedicated funding to create and share resiliency curriculums including civic and character education with parents and educators.
- Michigan’s investment in Transforming Research into Action to Improve the Lives of Students (TRAILS) aims to deliver resilience-focused lessons in classrooms. Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, TRAILS has seen a 1,000% increase in attendance of educators and counselors at school staff trainings.
Opportunity: Advocate for the role of life skills education through public campaigns and partnerships with relevant organizations
Governors and other state leaders are in a unique position to use their platforms to advocate for age-appropriate life skills education in schools, sharing experiences from their work or personal lives on the importance of teaching coping mechanisms from a young age. Public support from state leaders can go a long way to normalizing life skills education in schools. And states do not have to do this alone; partnerships with organizations, including non-profits and academic institutions, can help to craft relevant, impactful materials.
- New Hampshire Governor Chris Sununu implemented the Jesse Lewis Choose Love Movement curriculum in schools, containing evidence-based life skills strategies designed by an associated nonprofit.
- Healthy Minds, Thriving Kids curriculum, a comprehensive set of video and print life skills resources in both English and Spanish, disseminated to over 70,000 California educators in 2022.
- annual Governors’ Summit on Innovative Education, and in 2021, the summit featured a keynote address by Dr. Stuart Ablon, the director of Think:Kids in the Department of Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital, who emphasized that youth “lack skill, not will” when it comes to these life skills.
Opportunity: Encourage the teaching of practical life skills in out-of-school settings
Many valuable life skills are taught outside the classroom environment through sports, extracurricular activities or community engagement. According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), volunteering improves mental health; it is a way to build connections to reduce loneliness, develop self-esteem, reduce stress and find purpose. Maryland is a stand-out example of state leaders encouraging community involvement and is the only state which includes service-learning experiences as a condition of graduation. Since the class of 1997, approximately four million service hours have been provided to the community. Maryland Governor Wes Moore has also recently created the Department of Service and Civic Innovation to implement the country’s first state-run service-year option for high school graduates in Maryland and to encourage graduates to pursue civic options.
Priority: Implement mental health screening in relevant settings
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), approximately half of all lifetime mental health conditions begin before age 14; however, they regularly go untreated for years. To attend to these challenges sooner, the United States Preventative Services Task Force recommends, and the American Academy of Pediatrics endorses, conducting screenings for anxiety from age eight and major screening for depressive disorder or suicide risk from age 12. These screenings are often part of a child’s wellness check-up; however, not all children access or receive these services from a medical provider. Universally available, age-appropriate mental health screening for young people is an important secondary prevention mechanism. It can accelerate the detection and diagnosis of mental health conditions and enable earlier connection to care that helps prevent progression to more serious illness. Governors and other state leaders can consider how to implement school- and community-based mental health screenings on a statewide basis to provide access outside of clinical settings.
Opportunity: Allocate funding for mental health screenings in schools and other community settings
School-based screenings for physical health conditions, including hearing and vision loss, have long been accepted to address gaps in care. This should be the case for mental health conditions as well; however, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation, just one third of schools provide services that include mental health screenings for all students. Screenings in schools also offer the opportunity to assess school climate, overall well-being, and metrics of connectedness and belonging, both of which are predictive of student mental health and academic success as discussed above. Support for screenings also allows states to begin to focus on the connection between screening and services, ensuring that schools and community organizations have the resources they need to connect youth to quality care post-screening.
Multiple states have enacted legislation allowing school districts and/or individual schools to provide mental health screening to students, including: Colorado, Iowa, New Jersey and Utah. Other states’ legislation requires that these screenings are provided, including Illinois.
- National Center for Children in Poverty, more than 43 states use Medicaid to cover social-emotional screening of young children. More than 25 states allow for social-emotional screenings to take place in some sort of a nonmedical setting, like in the home, in a foster home, within early intervention services, or within an early care and education program.
Opportunity: Ensure mental health screenings reach high-risk populations
Youth from certain backgrounds are more likely to experience negative mental health outcomes. According to studies cited by Mental Health America, 65-70% of youth in the juvenile justice system have a diagnosable mental health condition. As stated by the National Conference of State Legislatures, as of 2019, up to 80% of youth in foster care experience significant mental health issues, drastically higher than the general population. Governors and state leaders have especially consequential influence over the mental health screening and services provided to youth involved in state systems, including justice involved youth, foster youth and youth with disabilities. Universally available mental health screenings should be prioritized for these populations to ensure coordinated statewide connection to care.
States are addressing this need. For example, Minnesota’s Children’s Mental Health Screening grant, launched in 2022 by the Minnesota Department of Human Services, provides funding to counties and tribes across the state to conduct children’s mental health screenings, targeting children ages three months to 17 years in Child Protective Services or ages 10 to 17 in the juvenile justice system. Currently, data is being collected in the Minnesota Social Service Information System to evaluate the impact of the grant and determine how much funding the awardees receive based on their reach.
High-risk populations are not limited to system-involved youth. In Montana, Governor Greg Gianforte announced a $2.1 million grant to fund free optional mental health and substance use screenings for all schools and same-day care for students flagged as being high risk for suicide. Of youth screened, nearly eight percent were identified with a recent high risk of future suicide, and of these at-risk students, 99.5% received same day follow up care by licensed clinicians.

Priority: Invest in crisis prevention and Response
A robust and multi-faceted crisis response system, with the requisite tools, processes and training for first responders, is a key component of crisis de-escalation and suicide prevention. The 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline, launched nationally in July 2022, forms an integral part of the crisis response frontline; however, Kaiser Family Foundation analysis shows that 988 in-state answer rates varied widely, ranging from a low of 51% to a high of 98%. This emphasizes the need for states to further integrate 988 into their larger youth mental health landscape to build a strong crisis response system with “someone to call,” “someone to respond” and “somewhere to go,” composing a comprehensive suicide and crisis prevention plan, including mobile response teams and community-based centers.
Opportunity: Allocate funding to ensure the 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline can effectively meet the needs of youth
State leaders can ensure that their local 988 systems have specific practices and training to respond to the unique needs of young callers. For example, in its 988 Implementation Plan published in 2022, Mississippi allocated $500,000 in SAMHSA grants and state appropriations to a Crisis Stabilization Unit for children and youth, including enhanced data collection and monitoring approaches for children at risk, and to develop an up-to-date referral approach to address the unique needs of the youth population.
States can also focus on underserved youth. Legislation enacted by Washington in 2021 requires its Crisis Improvement Strategy Committee to consider the unique needs of youth, including American Indian, Alaska Native and LGBTQ+ youth, and in 2022, Alaska was awarded a SAMHSA grant to target 988 messaging to at-risk youth.
Opportunity: Build mobile and community-based youth mental health crisis response and stabilization services
Crisis response systems that are embedded in the communities in which youth live, work and play are a critical component of a robust continuum of care. Mobile crisis response teams of trained clinicians that can be deployed to a young person’s home, school or other community location help stabilize youth and prevent hospitalization and incarceration and keep youth from harming themselves or others. Strong mobile crisis systems can further provide training for providers on youth-specific engagement strategies, highlight evidence-based models of care and facilitate connection to local providers. Over the past couple decades, states have been advancing these systems, particularly for youth.
Multiple states have statewide youth-specific mobile crisis programs. To highlight the outcomes of a few:
- Connecticut’s Department of Children and Families contracts with clinics throughout the state to provide no-cost statewide Mobile Crisis Intervention Services for youth under 18 years in-home and at school. Outcome reports have linked the crisis service to a 22% reduction in emergency department use, a reduction in student arrests by 40%, and higher functioning among youth after intervention.
- Oklahoma’s Youth Crisis Mobile Response is an integral component of Oklahoma’s youth suicide prevention effort, providing rapid mobile mental health services including crisis stabilization, counseling, and connection to follow-up services. Oklahoma has diverted 78% of youth from inpatient care, had fewer calls to the police, a reduction in Medicaid costs, and a positive change in youth behavior and functioning.
- Nevada’s Youth Mobile Crisis Program provided 86% of youth with a safety plan, resulting in 92% of youth avoiding emergency stays four months post-response.
- New Jersey’s Mobile Response and Stabilization Services provides 24/7 access to behavioral health workers and a variety of services including counseling, medication management, and care coordination. Since the start of the program, MRSS has kept 94% of children in their existing living situation at the time of service, including those involved in the child welfare system.
Opportunity: Implement state-wide suicide prevention plans throughout health care delivery systems and schools
There are central tenets to youth suicide prevention that can be adopted universally throughout the country, but it is also important for state leaders to consider their state’s diverse populations, specific youth needs, and unique state assets and partners to tailor prevention plans to their state’s youth. Relevant system stakeholders, including youth, need to be convened to develop and implement state-wide suicide prevention plans.
- Nebraska’s Suicide Prevention Plan, developed in partnership with The Kim Foundation in 2022, includes survey findings from over 500 diverse stakeholders from focus groups and online surveys. Once state-wide suicide prevention plans have been developed, state leaders can share guidance with counties and school districts on how best to implement them.
- New York’s Guide for Suicide Prevention in New York Schools provides best practices and resources for schools to implement suicide reduction through three tiers of universal, targeted and individualized interventions.
- Launched in 2020, Ohio’s Zero Suicide Pediatric Initiative is a partnership between the Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services, the Cardinal Health Foundation and the Children’s Hospital Association to provide training to hospitals on evidence-based and promising practices for suicide prevention.
Pillar 2: Increasing Awareness and Reducing Stigma
Mental health is front and center for today’s youth. By the end of 2022, TikTok videos with #mentalhealth had more than 45 billion views. According to the recent U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory on Social Media and Youth Mental Health, adolescents have been increasingly turning to social media for mental health advice, which can be both a safe space to find community as well as a source of harmful or misleading information. The number and diversity of mental health resources can be overwhelming as young people may not know where to turn for support and help. Additionally, individual, environmental or societal stigma can prevent youth from reaching out for assistance. A lack of understanding around the causes and symptoms of mental health can create stigma within youth and families, isolating youth who need help. Reducing stigma entails a whole family approach, and parents of youth with mental health concerns may also carry stigma or shame themselves. Increasing awareness of emotional well-being strategies and the spectrum of mental health needs improves our collective understanding and encourages young people and their families to seek information, recognize symptoms, learn about potential interventions and treatment, and access appropriate supports. Awareness can be promoted by educating young people and communities on mental health, promoting accurate and practical information and resources, and sharing personal stories of lived experience.
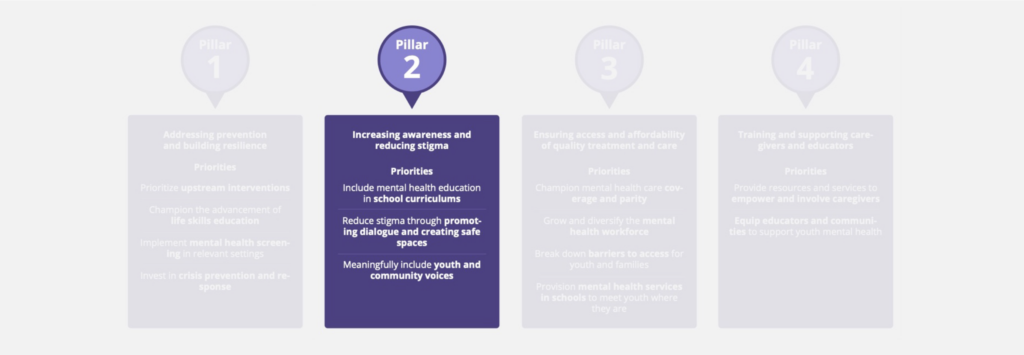
The existing leaders in this space are often youth themselves, and Governors can leverage the lived experience of youth to develop and improve policy that accurately reflects their needs. Younger generations are more comfortable talking about mental health than ever before, and Governors have the opportunity to build systems that are responsive to their concerns.
Priority: Include mental health education in school curriculums
Education helps to normalize mental health challenges and conditions that youth may experience. Including mental health as part of the school curriculum can help to standardize the level and type of content taught, and to ensure that it is age- and context-appropriate. Studies in the U.S. and Canada have shown that introducing mental health curriculum significantly predicted increases in positive attitudes toward mental health and reduced stigma.

Opportunity: Provide guidance and oversight for mental health curricula taught in schools
In 2018, New York and Virginia were the first two states to require mental health education in schools. Although some states encourage mental health curricula, the majority of states today have mandated it in either statute or regulations. For example, in 2019, Maine enacted legislation that requires mental health curriculum for K-12 that includes instruction in mental health and the relationship between physical and mental health to reduce the stigma associated with mental illness. Mandates are very important but should be supported with guidance and oversight from state leaders to ensure effective mental health education is taking place.
For example, New York’s School Mental Health Resource and Training Center helps schools to comply with its law by providing a Mental Health Education Readiness Guide to evaluate existing curriculum content as well as lesson plans. To assess the implementation of mental health curricula in schools, the New York State Comptroller performed an audit of school districts, finding variation in the materials between districts and the need for a formal mechanism to monitor implementation going forward. South Carolina’s Department of Education provides materials and standards for mental health curricula from seventhgrade onwards.
Opportunity: Orchestrate partnerships with state and academic groups to develop mental health curricula material
One way that states can support curricula implementation is through creating partnerships to develop robust materials. This can alleviate the pressure on school administrators to develop material themselves and help to promote age-appropriate and consistent quality across school districts. States can do this in different ways:
- Massachusetts’s Comprehensive Health Curriculum Framework was revised in 2019. The state Department of Education worked on this revision with a multidisciplinary committee in partnership with the Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education, the Massachusetts School Psychologists Association and the Massachusetts School Counselors Association.
- A Utah law enacted in 2022 requires the development of a youth behavioral health curriculum by the Education Department in conjunction with the University of Utah’s Huntsman Mental Health Institute. The multi-year program will draw on expertise from psychologists and trained educators at the Huntsman Institute to help students manage their mental and emotional health into adulthood. Utah dedicated $600,000 to develop and disseminate the curriculum to elementary and secondary schools in the state.
Priority: Reduce stigma through promoting dialogue and creating safe spaces
Compared to previous generations, young people today are much more open to talking about their mental health and want to play an active role in reducing the social, self and structural stigma surrounding their mental and emotional health. However, youth mental health stigma is a reality across different settings. Within the home, a cultural disconnect or generational divide can make it difficult to talk about mental health, and outside the home, misconceptions continue to pervade attitudes in schools and colleges, places of worship and workplaces. There is a lot that state leaders can do to promote acceptance of mental health challenges and conditions, encourage young people to talk about them, and create avenues – digital or in person – for youth to turn to when they need help.
Opportunity: Invest in anti-stigma campaigns to reach youth populations through diverse and inclusive messaging
Research from Tulane University showed that 90% of teenagers who are taking psychiatric medications displayed at least one of the three measured stigma themes: secrecy, shame and limiting social interaction. Effective anti-stigma campaigns incorporate the lived expertise of the youth they serve to build culturally relevant programs that address the realities of the communities in the state. States regularly launch anti-stigma campaigns, for example:

- Georgia’s 2022 #FreeYourFeels campaign encourages youth to share their real feelings online, and Tennessee’s educational website shares information about the different types of stigma and the importance of confronting it.
- Ohio’s “Life is Better With You Here” campaign aims to reduce the high suicide rate of Black youth with pop-up events established in communities and colleges.
Opportunity: Champion the use of digital tools as safe spaces to enable students to report mental health issues and be connected to help
Adolescents may feel more comfortable sharing their mental health issues, or those of their peers, anonymously in digital spaces. State leaders can consider developing and supporting digital tools for use in schools; importantly, apps need to be integrated into the system of care so that youth’s concerns are taken seriously and, if appropriate, they can be connected to clinical help. Further, states can periodically monitor and evaluate outcomes from these platforms to determine which digital tools are most effective in reaching youth and connecting them to the right services and supports for their needs.
- Colorado’s iMatter program, established in 2021 through legislation that initially appropriated $9 million in state funding, includes an online screening tool for youth up to age 21, provides up to six free virtual therapist visits, and has successfully engaged youth and delivered services.
- In 2019, when serving as attorney general, Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro launched Pennsylvania’s Safe2Say Something, a $1.6m partnership funded by the State and Sandy Hook Promise. Although built for the purpose of reporting possible threats of school violence, approximately 75% of the first 100,000 tips have been about mental health issues. More than 26,000 tips were received in the 2021-2022 school year, an increase of 140% year over year.
- Utah’s SafeUT app connects students, parents/guardians and educators with licensed counsellors from the University of Utah’s Huntsman Mental Health Institute to share any crisis or concern 24/7. Funded by the state and developed via a public-private partnership, over 95% of all Utah K-12 schools and universities have been enrolled in SafeUT with over 880,000 students having access to the app. From 2021 to 2022, SafeUT received over 25,000 total chats and tips along with one million back and forth chat messages.
Priority: Meaningfully include youth and community voices
Listening to the lived experience of youth and their communities and engaging them in policy development enables more relevant action from Governors and other state leaders. Community-based organizations are often well-trusted and have a deep knowledge of the needs of the people they serve and knowledge of how best to address them.
Opportunity: Include young people in the development of youth mental health programs and policies
Those with lived experience of mental health problems should have a real seat at the table, not only when problems are being discussed, but also when programs are being designed and decisions made. Many states and territories have a youth council:
- New Mexico’s Indigenous Youth Council provides youth-specific recommendations to the state Indian Affairs Department (IAD) for behavioral and mental health needs in tribal communities.
- Vermont’s State Youth Council advises the Governor and general assembly on issues including mental health, education, equity and climate change. Maryland’s Youth Advisory Council also jointly advises the Governor and state legislature. Arizona’s Governor’s Youth Commission has five workgroups dedicated to distracted driving, domestic violence, mental health, education and substance use. American Samoa’s Youth Council meets monthly and serves as the voice of youth to the government.
- Valuing the expertise that comes from lived experience, state leaders can look to reimburse youth for their contribution. For example, Nebraska’s Student Advisory Board of the Behavioral Health Education Center has established paid leadership opportunities for students of color pursing a degree in behavioral health to contribute their perspectives on state health care policies.
Opportunity: Consider diverse perspectives from youth-focused community organizations
It is important to ensure that community organizations have a seat at the table on advisory and other committees to incorporate their valuable perspective. Funding the work of existing community-based organizations’ youth mental health efforts is another way to drive impact; solutions to the youth mental health crisis exist within communities, and there is a lot that state leaders can do to elevate them.
- In 2021, Oregon’s Health Authority funded The Coalition of Communities of Color to engage with different community groups to improve the access, utilization and outcomes of behavioral health for Black, Indigenous and people of color (BIPOC) communities.
- Kansas’s School Mental Health Advisory Council creates partnerships between parents, educators, providers, legislators and community partners. It also provides a platform for these stakeholders to advise the state board of education on school mental health.
Pillar 3: Ensuring Access and Affordability of Quality Treatment and Care
According to recent data from the CDC, 15% of children aged 5 to 17 had received mental health treatment within the past year. On average, according to the National Alliance on Mental Illness, it takes 11 years after the onset of mental health symptoms for individuals to receive treatment, and access and affordability challenges contribute significantly to this delay. Ensuring access requires public and private coverage across the continuum of quality youth mental health services, treatment and care to be available where and when required (with appropriate treatment pathways and referral loops), sufficient capacity for inpatient, outpatient and intermediate services in brick-and-mortar settings and in staff, and the use of telehealth and digital tools where appropriate to increase convenience and minimize wait times. Increasing affordability means that young people in need receive treatment regardless of insurance coverage and acuity, means there is parity between benefits and coverage for physical and mental health, and means reimbursement approaches incentivize appropriate and high-quality care. High-quality care is also enabled by integrated systems with well-coordinated handover points.
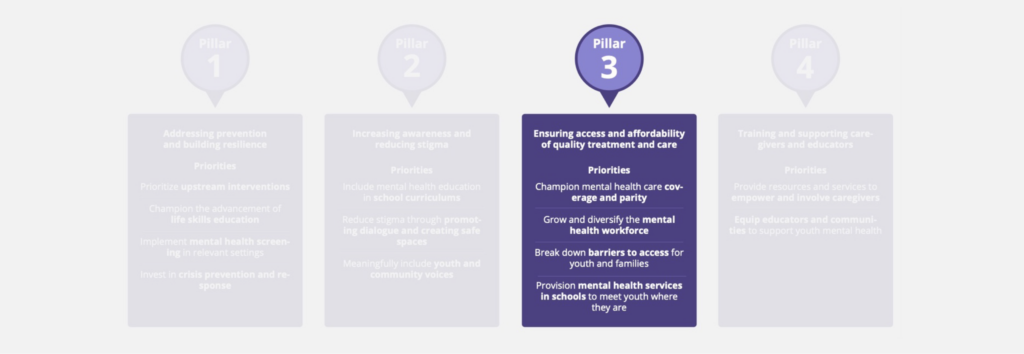
It is important to note that this pillar focuses on access to quality care. For the purpose of this Playbook, high-quality care is care that effectively meets the needs of each youth, as determined by the youth, their family and their care team. Governors and state leaders have the opportunity to identify and prioritize high-quality care within their states by listening to the voices of youth, families, providers and community leaders, and by collecting data on key metrics to assess the outcomes of care strategies and the value they offer to families.
Priority: Champion mental health care coverage and parity
Accessibility of mental health care is often related to the affordability of that care. Medicaid agencies and commercial insurers play a critical role in increasing access to and parity for mental health care, but gaps remain due to insufficient reimbursement rates across public and commercial insurance and high out-of-pocket costs. High out-of-pocket costs for treatment can add to the burden for families struggling with mental health concerns, made worse for those who are uninsured or underinsured. However, robust access to affordable care cannot exist without a sufficient pipeline of youth-focused mental health workers as addressed in another priority.
Opportunity: Bolster Medicaid and CHIP coverage for and access to mental health care for eligible young people
Medicaid is vital to the health and wellness of young people and covers 35 million children across the country, over 40% of its entire enrollee population. By expanding Medicaid to cover a full range of medically necessary services from prevention to crisis care, states can supplement and amplify their investments in youth mental health. Encouraging provider acceptance of Medicaid through increasing reimbursement rates for mental health services is particularly important for vulnerable youth.
Multiple states have enacted Medicaid State Plan Amendments to allow schools to bill for all medically necessary services provided to Medicaid-enrolled students, including all treatments required under the Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment (EPSDT) mandate. The EPSDT mandate requires states to provide comprehensive health care services to children and adolescents who are eligible for Medicaid. Personal care services, transportation and applied behavioral analysis can be billed to Medicaid in a school-based setting as needed. Recent federal guidance from the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) provides new flexibility to cover a range of school-based mental health providers increasing access to mental health care services.
- The Healthy Schools Campaign provides information on the multiple states that have enacted Medicaid State Plan Amendments to allow schools to bill for all medically necessary services provided to Medicaid-enrolled students, including all treatments required by the EPSDT Program.
- Another barrier to care can be the requirement to have a formal mental health diagnosis in order for services to be covered. If certain criteria are met, California and Massachusetts allow youth to access Medicaid mental health services without requiring a diagnosis, thereby reducing stigma and other barriers to youth getting therapeutic support.
Throughout this Playbook, several state programs that leverage Medicaid funding in innovative ways are highlighted. The landscape and needs of each state are different, and Governors have the opportunity to encourage state agencies to leverage Medicaid to best fit their state’s needs.

Opportunity: Enforce parity from payors for physical and mental health services
According to Mental Health America, 1.2 million youth covered under private insurance do not have coverage for mental health care. This is despite federal legislation passed in 1996 (the Mental Health Parity Act) and 2008 (Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act) that requires insurers to cover mental health and substance use disorder benefits under the same terms as physical health benefits, following which 37 states have enacted laws codifying similar requirements at the state level. A report from the Council of State Governments highlights leading states’ efforts to shape coverage, provide a model for federal legislation, facilitate implementation of federal laws and ensure insurance market compliance. However, challenges still exist with compliance efforts on parity. States can encourage federal regulators to allow states to lead in ensuring plan compliance with mental health parity laws and implement state-level legislation and regulation to drive parity. Robust mental health agendas rely on partnerships within and outside of the public sector, and Governors have the opportunity to build collaborative partnerships with health insurance organizations to create a statewide vision on strengthening youth mental health.
- The Illinois Department of Insurance was given explicit oversight authority of school, municipal and county plans in the state to ensure compliance with parity. It performs comprehensive market conduct examinations to ensure health insurance companies are following parity laws and requires both commercial and Medicaid plans to submit parity compliance analyses to the state annually.
- New York’s State Office of Mental Health Parity Compliance Toolkit supports the understanding of mental health and substance use disorder parity among insurers, providers and consumers by providing definitions and resources surrounding the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act in state context. New York State has also conducted rigorous analyses of Medicaid managed care plans’ parity compliance.
- Texas’sHB 2595, signed into law in 2021, created a parity complaint portal with basic tracking and reporting features to ensure an enrollee’s complaint can be filed and followed up on, and requires annual reporting of parity metrics.
- Arizona’s Jake’s Law prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage for services covered by a plan because they are delivered in an educational setting, created the Children’s Behavioral Health Services Fund and provided $8 million for behavioral health services for children who are uninsured or underinsured. It also requires health plans to submit parity compliance analyses to the state.
- Massachusetts legislation enacted in 2020 requires coverage for same day care, specifically prohibiting insurers from denying coverage for mental health services and primary care services solely because they were delivered on the same day in the same facility.
Priority: Grow and diversify the mental health workforce
The national shortage of youth mental health professionals across all specialties, credentials and geographic regions continues to impede access for youth to treatment and care. According to a policy brief from the University of Michigan School of Public Health, the U.S. needs more than 28,000 additional child and adolescent psychologists by 2030, an increase of over 25% of today’s workforce. These shortages particularly impact intensive outpatient programs or specialized care, rural communities and low-income urban areas.
Opportunity: Expand pathways and entry points into the youth mental health field
The NGA Center for Best Practices is working with over 20 states in the Next Gen Healthcare Workforce Project and Knowledge Exchange Network to strengthen and expand the next generation of healthcare workers, including for mental health. Young people in high school and college can be educated and inspired to follow a career in mental health, both clinical and non-clinical, but action is also needed to support these career paths through programs including loan repayment models and apprenticeship opportunities, notably to incentivize service provision in under-resourced areas.

Many states are testing out different approaches to incentivize and develop the mental health workforce of the future:
- Michigan’s student mental health apprenticeship retention and training (SMART) internship grant program provides a $25 per hour stipend (up to $15,000 annually) for psychologists-in-training during their field education in public schools.
- Oregon’s Mental Health Emergency Act diversity initiatives provide incentives to retain BIPOC and rural behavioral health providers and encourage them to practice in underserved areas to help eliminate health disparities.
- Georgia’s Transformative Experiential Training grant aims to place a gender-, racially- and ethnically diverse group of trainees in a hub-and-spoke model to link interdisciplinary specialist teams virtually to serve high need areas.
Loan repayment is also an impactful lever. Behavioral health professionals in New Jersey can have up to $150,000 of their student loan balance paid off in exchange for six years’ work at an approved community provider, and those who primarily work with children and adolescents can receive supplemental grants up to $30,000. Texas’s and North Dakota’s loan repayment programs also encourage mental health professionals to practice in provider shortage areas.
Opportunity: Review licensing regulations and requirements for mental health professionals to reduce barriers to practice
According to the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatrists, child and adolescent psychiatrists are unevenly distributed across the map. Ratios per 100,000 children range by state from four to 65, with a national average of 14, compared to the required 47. Exacerbating this uneven distribution are administrative burdens that mental health professionals face in obtaining licenses to practice within their state and especially across states, limiting their ability to provide care to youth in need. Cross-state practice is particularly important for military families and college students who often move across state lines as well as for youth of color seeking a mental health professional who looks like them.
- Minnesota legislation enacted in 2022 establishes a workgroup including mental health providers from diverse cultural communities and representatives from graduate programs to identify barriers to licensure, collect data on the number of individuals graduating but not passing licensing exams and develop recommendations for creating alternative pathways for licensure in mental health professions.
- In 2021, Utah Governor Spencer Cox formed the Office of Professional Licensure Review to review and reduce barriers in occupational licensing. In November 2021, the first hearings started to prepare a report for the state legislature to act on reducing barriers to mental health worker licensing for social workers, clinical mental health counselors, psychologists, marriage and family therapists, substance use disorder counselors, recreational therapists and state certified music therapists. The proposed report, to be published in the summer of 2023, will include a policy landscape; impact on consumers, practitioners, and the state and recommendations to implement licensing changes that allow professionals to work to the full scope of their licensure .
- Across states, the multi-state Counseling Compact allows professional counselors to practice in other compact member states without the need for multiple state licenses. Providing increased continuity of care and access for children/adolescents who live in mental health care deserts, counselors can practice both in-person and through telehealth if they hold a valid, unrestricted home state license in a compact-member state. With 25 states currently in the compact, there are an additional 15 states with pending legislation to enter the compact.
- The Psychology Interjurisdictional Compact (PSYPACT) is another interstate compact designed to facilitate the practice of telepsychology and the temporary in-person, face-to-face practice of psychology across state boundaries, with 39 current effective state members.
Opportunity: Train pediatric primary care physicians to provide youth mental health care and support linkages to specialty care providers to amplify reach
Integrated care models for youth mental health care can help to mitigate the shortage of specialist clinical providers and provide patients with more coordinated care. Increasing the competency and capacity of primary care providers (PCPs) on youth mental health, notably screening and early identification, enabling the co-location of both mental and physical health services and connecting PCPs with psychiatrists, psychologists and other behavioral health professionals are ways that states can better equip PCPs to respond as appropriate to the significant number of young people in need. States can also expand consult lines to support primary care providers with mental health screening, treatment plan development and prescribing.
- New York’s Project TEACH provides training to providers who treat children and adolescents to assess, treat and manage mild-to-moderate mental health concerns.
- Washington provides grants to primary care practices serving children and youth to establish behavioral health integration, including training, technology support, physical space modifications and recruitment of behavioral health professionals.
- Oklahoma’s Project ECHO is a hub-and-spoke model that educates local providers about providing pediatric mental health care, often in under-served areas. A specialist team disseminates best practices through case-based learning and upskills PCPs through guided practice.
- Missouri’s Child Psychiatry Access Project (MO-CPAP) connects PCPs to mental health coordinators or child and adolescent psychologists. Among the 400 enrolled PCPs, nearly all reported improved patient care, and all said that they would use the service again if needed. In 2022, MO-CPAP expanded to schools.
- The U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) has a Pediatric Mental Health Care Access Program that provides funding and technical assistance to states, regions, territories and tribal partners to support providers working with children in primary care practices, schools, emergency departments and other settings to help children with mental health conditions.
Opportunity: Diversify the pipeline of youth mental health professionals to better reflect the communities in which they operate
According to 2021 data from the American Psychological Association, about 81% of the U.S. psychology workforce is white. Although this share is decreasing, the workforce lacks adequate representation of people of color, LGBTQ+ people and people with disabilities. The demand for diverse mental health professionals – notably those with a youth focus – far outstrips the supply, and there are often long waitlists for people in need to see a psychologist or psychiatrist who shares their cultural background and lived experience.
Massachusetts’s Mental Health Workforce Pipeline Pilot Program aims to foster a culturally, ethnically and linguistically diverse behavioral health workforce. In 2022, legislation was enacted requiring the State Board of Professional Counselors and Therapists, the State Board of Examiners of Psychologists and the State Board of Social Work Examiners to have at least three members who are from underrepresented communities. Colorado’s new Behavioral Health Administration created a multi-faceted plan to increase and diversify the behavioral health workforce through funding appropriated from the American Rescue Plan Act. The agency is designed to be the single entity responsible for driving coordination and collaboration across state agencies to address behavioral health needs.
Opportunity: Require mental health professionals to complete cultural competency trainings
Cultural competency training is especially important when considering that a person’s perception of mental health, including stigma, is often influenced by their cultural identity and social value. According to the American Psychological Association, nine states mandate psychologists to complete a course in equity, diversity and inclusion as part of their continuing education requirements. A number of states have cultural competency training requirements for a broader set of clinicians, including:
- Minnesota’s Culturally Informed and Culturally Responsive Mental Health Taskforce was established by state law in 2022 to recruit mental health providers from diverse communities, train all mental health providers on cultural competency, assess the extent to which mental health provider organizations embrace diversity and increase the number of mental health organizations that are led by people of color.
- Oregon law requires licensing boards to create a cultural competency requirement based on race and gender-based disparities in healthcare, including youth-specific cultural competency, and review their curriculum for compliance using professionally relevant and nationally recognized organizations.
Opportunity: Fund peer-support models for youth mental health
Peer support models have gained significant traction nationally, and adolescent brains are especially responsive to peer influence, which can be highly beneficial in terms of youth mental health if teenagers’ peers have been trained to support. Children and adolescents are also often more likely to take their concerns to a friend than an adult. Governors can help equip youth with the tools to offer protective and effective support to their peers.
According to SAMHSA, 49 states have established certification for peer support specialists.California and New York legislation allow certified youth peer support services to be reimbursed through Medicaid. North Carolina launched NC Voices Amplified in 2022 to provide training, technical assistance and other resources for an expanding workforce of family and youth peer support providers across the state. Georgia’s Certified Peer Specialist – Youth designation is a young adult between the ages of 18 and 30 certified by the Department of Behavioral Health and Developmental Disabilities who has lived experience of either a mental health condition and/or substance use disorder as a youth and is practicing recovery as related to that condition. Wisconsin has over 200 schools with student-led peer support wellness programs.
Priority: Break down barriers to access for youth and families
Today’s youth mental and behavioral health landscape is fragmented and uncoordinated, and young people and their families are forced to be extremely resilient and resourceful to access care. Even when services are available, access challenges including finding transportation and balancing competing needs can delay receiving treatment. Practices such as prohibiting payment for medical and mental health services on the same day for the same patient fragment care and impede integrating medical and mental health care. Strong community- and school-based systems, with accessible patient pathways, can prevent escalation that would require utilization of crisis and/or inpatient services.
Opportunity: Ensure clear entry points, case management, and handovers within the youth mental health system
A significant driver of the youth mental health crisis is the complexity of the system, which often creates insurmountable challenges for families seeking treatment for their children who are at risk of “falling through the cracks” when shifting from one acuity level to another. Lack of communication between mental health systems and schools and primary or specialty care physicians may hinder effective post-acute care and result in potentially preventable readmissions.
- Illinois’s Children’s Behavioral Health Transformation Initiative launched in 2022. It recommended the development of a centralized “Care Portal” as a resource for families to seek cross-agency mental health services. It also recommended conducting regular data reviews to inform capacity adjustments (i.e., number of psychiatrists or counselors needed in an area) and implementing resource referral technology for increased patient access.
- Indiana’s Child Mental Health Wraparound (CMHW) centralized its “point of entry” for youth and families for community-based mental health services and state-funded homes. Indiana’s Division of Mental Health and Addiction chose non-profit Child Advocates to administer CMHW. Families can call one phone number (211) to be assessed, triaged and connected into the CMHW program, if eligible, or otherwise be directed to other resources and information. Indiana Medicaid covers the provided services. Child Advocates will manage all incoming referrals for the CMHW program in all of Indiana’s 92 counties and assist youth and families with the application process for children on Medicaid.
Opportunity: Support the use of telehealth in relevant settings
Building the capacity and infrastructure for mental health services can be a challenge. The systems that enable advancements in digital mental healthcare have not kept up with the surging demand for care, and innovation can be blocked by a lack of infrastructure or burdensome and outdated regulations. Telehealth can be a powerful tool to provide culturally-representative, affordable and stable care. Access to telehealth offers unique benefits to transient youth, like college students, those in military families, the foster care system or in rural and underserved areas. Telehealth can be leveraged in home- and community-based services and can also be a critical tool for schools. According to the Institute of Education Sciences, in 2022, 17% of public schools had implemented some form of telehealth services, a number that is expected to grow as more students seek mental health services post-pandemic.
- Texas provides telehealth and telemedicine services in schools through the Texas Child Health Access Through Telemedicine (TCHATT) program and to primary care providers through the Child Psychiatry Access Network (CPAN).
- New Jersey dedicated $26 million in funds from the American Rescue Plan Act to support access to mental health care for college students, including $10 million for a statewide tele-mental health partnership with Uwill to provide all students at all public and independent institutions with a public mission in the state with access telehealth services for free.
- South Dakota released guidance on how school districts can integrate free telehealth services in schools through a partnership with the Department of Social Services and the state’s Community Mental Health Centers. South Dakota’s Juvenile Justice Reinvestment Initiative offers family-based therapy, aggression replacement training, and substance abuse treatment through telehealth for justice involved youth.
- Mississippi is providing access to school telehealth services statewide starting August 2023 through a $18 million telehealth grant approved by the Mississippi Department of Education for University of Mississippi Medical Center.
- Pennsylvania has entered into a $3 million one-year contract with Kooth, a digital mental health platform, to provide free telehealth services to 30 school districts across the state.
- Wisconsin Governor Tony Evers awarded $2.5 million in American Rescue Plan Act funding to five organizations to increase access to child telepsychiatry services
Opportunity: Create and support youth centers that provide mental health services in their communities
Children and adolescents often rely on clubs, organizations, sports teams and safe spaces within their communities to go to after school. These spaces can be highly suitable to provide appropriate mental health supports, such as counselling, and to connect youth to care in more acute situations.
- California’s allcove centers provide free or low cost mental and physical health services, education support, career coaching, and peer, family and social supports in youth centers catering to those aged 12 to 25 years.
- Georgia’s Mental Health Resiliency and Support Clubhouses and Youth Peer Drop In Centers provide skills development programs for young people to manage mental health symptoms and learn coping skills.
Priority: Provide mental health services in schools to meet youth where they are
There is an opportunity to meet children where they are: in school, for seven hours a day, five days a week. Established and often well-trusted relationships between schools, families and community-based organizations can facilitate appropriate resources and services. Data from the U.S. Department of Education shows that 96% of all public schools reported offering at least one type of mental health service. However, according to Effective School Solutions, only 40% of school administrators said they were highly confident to tackle mental health challenges.
Opportunity: Increase the number of school-based mental health providers
Research has shown that embedding mental health services into schools reduces the stigma of accessing services, increases mental health care utilization and improves overall youth mental well-being. States are focusing on increasing the number of mental health professionals within schools. For example:
- Delaware established a three-year phased approach to reach a ratio of one full-time school counselor or social worker for every 250 students and one full-time school psychologist for every 700 students in grades K through eight.
- New Mexico has a five-year plan to hire over 400 school-based mental health providers in public schools, with a strong focus on addressing equity gaps in mental health options for Indigenous students and those who live in rural areas.
- North Carolina used American Rescue Plan Act funding to establish a need-based grant program for schools to hire psychologists in response to COVID-19.
- U.S. Department of Education is supporting states’ efforts to expand school-based mental health providers through $188 million in funding from the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act.
Opportunity: Build capacity through school-linked partnerships with community providers
Schools cannot do this alone; they need administrative support and capacity expansion through connection to community-based services. These strategies can be employed not in place of outpatient or clinical care, but alongside it, to build a robust scale of services.
- Alabama addresses this “top down,” requiring a school mental health service coordinator in every school district, to set up mental health awareness events, hold small group sessions with students and connect families with professional mental health services.
- Kansas’s Mental Health Intervention Team program links local education authorities with community mental health centers and provides a system of payments and outcomes data reporting through the State Department of Education. Outcomes from the pilot year indicated over 1,700 students served through the program and improvements in academics, attendance, behavior and overall school climate.
- Georgia’sAPEX program is a partnership between community mental health providers and local school districts to provide mental health services for K-12 students. The program has provided first-time mental health services to approximately 14,000 students.
Pillar 4: Training and Supporting Caregivers and Educators
Caregivers and educators play a vital role in supporting young people’s mental well-being by observing warning signs of mental health challenges and conditions and steering young people to care before crisis point is reached. However, they cannot do this unsupported. Youth-facing adults need to be trained to recognize symptoms and appropriately react in a supportive manner. Currently, there is significant variation in mental health literacy across caregivers and educators who face difficulty with their own mental and emotional health management, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. The country is also simultaneously experiencing increased rates of educator burnout. An ideal target state is one in which all caregivers and educators are empowered to appropriately support young people with their mental health needs, workplace accommodations, community support, accessible and affordable care for themselves, and relevant in-home, in-community, and in-classroom services.
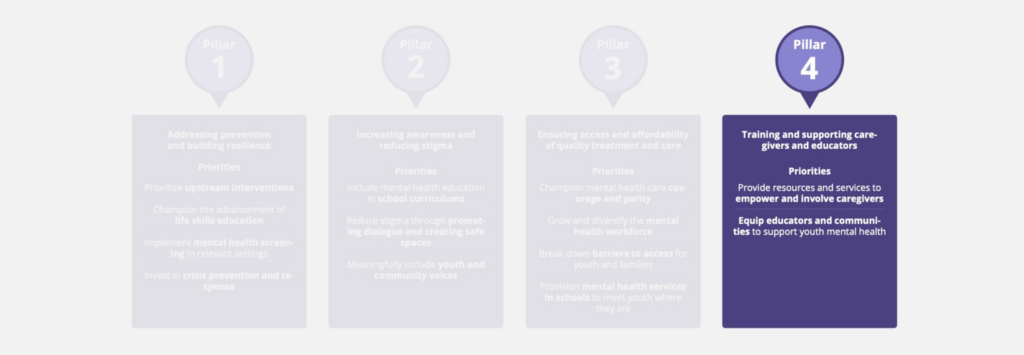
Priority: Provide resources and services to empower and involve caregivers
Parents and guardians play a fundamental role in developing their children’s mental well-being and supporting them when they are facing challenges. Caregivers know their children best but can use help to understand how to talk to their children about mental health, recognize and respond to changes in behavior at home, and what to do about them. Caregivers also face significant barriers when navigating the complex mental health system to secure care for their child. In a study investigating perceived barriers to access to youth mental health care, parents commonly reported lack of information and issues with health care professionals taking them seriously or referring them to specialized supports.
Opportunity: Share and expand supports to help caregivers manage their children’s youth mental health challenges
Eighty-five percent of parents in the U.S. are worried about depression negatively impacting the lives of their teenage children according to research done in 2022 by the Kaiser Family Foundation. Having a child with a youth mental health challenge can be stigmatizing due to misconceptions and caregivers can benefit greatly from peer support from those who have been through similar experiences.

- Montana’s Department of Public Health and Human Services distributed $1 million in innovation grants to engage family members of youth served through the state children’s mental health system and who are facing out-of-home placement. The funds focused on improving the engagement, involvement, and capacity of families to provide for the care and support of their child following any out-of-home placement as well as improving ways to engage family members in community- and home-based care to prevent the need for out-of-home placement.
- The District of Columbia’s Parent Support program launched in 2019 and includes a monthly online support group offered via video call in English and Spanish. There is also a mental health hotline for parents to speak with licensed clinicians for immediate support to discuss coping strategies, address crisis situations and resolve family stressors. The program also has a bilingual on-demand video library. In 2021 alone, this group provided webinars to approximately 2,000 individuals and 2,500 outreach services to individuals and created a website of English and Spanish resources for parents to use to support their well-being.
- Kentucky’s Family to Family Health Information Resource Centers offer mental health support through health consultants, with peer liaisons available for conversation and support in accessing services including formal support groups.
- Louisiana’s Be Engaged Birth-12 Framework provides a roadmap for effective engagement between schools and caregivers, highlighting family engagement opportunities throughout a child’s progression from early childhood through high school.
- In late 2022, the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources Kids Thrive Collaborative launched weekly virtual sessions for parents and caregivers of children to share information on community-based mental and behavioral health services.
Opportunity: Create holistic systems of care that include culturally relevant wraparound support for caregivers and integrate caregivers in mental health care to improve youth outcomes
Caregivers need information and support, but they also need effective and holistic systems of care that include them in the care and treatment journey. Systems of care help families navigate this journey without expecting them to “quarterback” it. Multiple states have an integrated system of care to support this, for example:
- New Jersey’s Children System of Care (CSOC) offers care for all youth in New Jersey aged 5 to 21, at no cost to the family, regardless of insurance status or income. Funded through a combination of Medicaid, state funding and family insurance when available, CSOC includes care management organizations that holistically help families identify needed care and family support organizations that act as peer supports for parents. Care provided for youth includes in-community, in-home, and out-of-home treatment and support, including Mobile Response and Stabilization Services and respite care for families with youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Evaluation data has shown that 93% of families receiving CSOC services have a better understanding of their youth’s needs, and 94% feel better able to navigate and manage their youth’s mental health needs.
- Idaho’s system of care, Youth Empowerment Services (YES), includes a Child and Family Team that partners with a family and youth to create a coordinated care plan across all health providers in the youth’s community. Eighty-three percent of parents state that the program empowered their family as the main decision-makers about care and 76% said providers were acting in a beneficial manner for youth. Youth receiving court-ordered mental health services has decreased by 48% in Idaho since the launch of YES.
- States can fund evidence-based training centers to ensure caregivers and families have the proper skills to deliver quality care that is safe. In Maryland, the Maryland Coalition of Families provides robust training opportunities for parents and caregivers to support their navigation of the mental health services and advocacy for an improved system of care.
Priority: Equip educators and communities to support youth mental health
Young people are in day-to-day contact with various people outside their families who can play a critical role in their mental health. Educators are key youth-serving adults due to the frequency of interaction with their students, but the “village” includes faith leaders, sports coaches and a host of others who have regular contact and connection with children. Educators and community leaders are often the first lines of defense in recognizing the symptoms of mental health challenges in youth and can play a pivotal role in supporting their mental well-being and connecting them to care.
Opportunity: Equip educators to recognize warning signs of mental health challenges in their classrooms
Early identification of mental health challenges is not only key to preventing mental health decline and crisis among youth; behavioral issues in the classroom or poor academic performance often stem from or are otherwise connected to students’ mental health. By equipping educators and other school staff to identify mental health needs, state leaders can help improve academic achievement, classroom environments, and both student and educator success and well-being. For example:

- North Dakota’s Department of Health and Human Services’ Behavioral Health Division has made online, role-playing simulation technology available to help school personnel recognize signs of distress and models conversations for approaching students and discussing concerns, as well as making referrals for both parents and students to appropriate resources.
- Rhode Island, enacted legislation in 2021 that requires the Department of Education to adopt rules and regulations supporting annual suicide prevention and training for public school personnel, including educators, administrators, custodians, lunch personnel, substitutes, nurses and coaching staff (including volunteers).
- In South Dakota,all educators and education professionals are required to participate in a minimum of one hour of suicide awareness and prevention training. The state Board of Education identifies evidence-based resources that fulfill suicide awareness and prevention training requirements and make these lists available to school districts.
Opportunity: Provide resources for educators to support their own mental health needs and cope with burnout
Educators are often exhausted and underprepared to support students’ mental health, especially in the era following the COVID-19 pandemic, while also coping with their own stressors. An early 2021 survey by the RAND Corp. found that educators are almost twice as likely to experience frequent job-related stress and nearly three times as likely to experience symptoms of depression than the general population. Educators need support to manage their own mental health so that they have the capacity to help their students to do the same. Some states have done this through legislation:
- Washington law enacted in 2021 acknowledges the significant toll secondary traumatic stress has on educators, and subsequently students, and focuses on the adoption of policy and procedures so schools can reduce staff turnover, improve student outcomes and model healthy behaviors for the school community.
- Illinois law enacted in 2022 requires all school districts to include mental health as part of their current negotiated sick days for full-time employees of the district. Two days are currently allowed, but more may be permitted with a note from a mental health professional.
- States can also support educators through providing resources. As of 2023, Hawai’i provides free mental health resources for stress, anxiety and depression via a confidential, clinically-validated app based on the principles of cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness and meditation. The app provides resources such as daily mood tracking, guided journeys, coping tools, meditations, progress assessments and the ability to reach out to an anonymous community of peers for support.
Opportunity: Support faith- and community-based mental health training and programs
Every young person affected by mental health challenges should be surrounded by a community that cares. According to SAMHSA, many people turn to trusted leaders in their communities before they turn to mental health professionals. Recognizing this, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Center for Faith-based and Neighborhood Partnerships published a guide on youth mental health and well-being in faith and community settings. Faith leaders should be equipped through training and resources to play a positive role in reducing the stigma around mental health in their communities and helping young people to navigate care.
States can empower faith leaders in different ways. One example is Missouri’s Bridges to Care and Recovery program, which aims to mobilize churches in St. Louis’s African-American faith community to support behavioral health assessment, treatment and recovery. “Church engagement” requires congregants to complete 19 hours of training to receive the designation of “behavioral health friendly” church, with monthly meetings and further trainings for ongoing support. “Wellness champions” are also supported through the program; these are faith-based volunteers who have completed at least 14 hours of training and have made a commitment to reduce the stigma of mental health conditions.
Way Forward and Supporting Next Steps
Despite the challenges that lie ahead to reverse the downward trajectory of youth mental health and strengthen the complex systems across the country, significant progress has already been made by states to identify and implement solutions that make a difference in the quality of young people’s lives and those of their families and wider communities.

When developing the framework for the 2022-2023 Chair’s Initiative, New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy identified four themes that became the pillars of the work: addressing prevention and building resilience, increasing awareness and reducing stigma, ensuring access and affordability of quality treatment and care, and training and supporting caregivers and educators. These pillars represent a comprehensive effort to capture the urgency and scope of this issue. Strengthening Mental Health: A Governor’s Playbook is the culmination of the 2022-2023 NGA Chair’s Initiative, but the policy, advocacy and program work of a multitude of public and private sector organizations will need to continue and adjust to changing circumstances for years to come. Governors have the opportunity to protect and cultivate the wellness of youth in their state and build a stronger path to a healthy future.
This Playbook offers a set of emerging best practices across the four pillars, though it does not, as it cannot, represent all of the innovations that states are spearheading around youth mental health. Strong mental health agendas incorporate and elevate the voice of youth, and valuing their lived expertise is critical to create a system that reflects their needs. The data speak for themselves; children and youth of all ages are struggling, and some are hurting worse than others. Each youth’s journey with their mental health and well-being is unique, and each state has its own landscape and priorities. Governors have the opportunity to devote time, attention and resources to develop supports for youth of all needs – saving the lives of our most vulnerable youth and championing a holistic system around mental wellness.
The current concerns around youth mental health may seem daunting, but there is so much hope. Innovators driving meaningful change in youth mental health are already embedded in schools, leading advocacy and community organizations, serving as health care providers, steering insurance organizations, celebrating their high school graduations and leading states as Governors. The National Governors Association and Governor Murphy are grateful to have connected with many of them in the development of this Playbook and will continue to elevate their invaluable expertise.
The goal of this Playbook is to offer a starting point for Governors to implement change in their own states; these pillars only stand if we build something to support them. If a Governor’s office is interested in any of the priorities, opportunities or examples highlighted above, they can visit the NGA website for additional state examples and resources from the Chair’s Initiative thought partners. Policymakers can also reach out to the NGA team for support. The National Governors Association exists to serve the needs of all 55 Governors in the states and territories, and NGA looks forward to supporting the states’ work to strengthen youth mental health and wellness for years to come.
Acknowledgements
The National Governors Association and Governor Murphy would like to thank the funders, partners, thought leaders and organizations that contributed to the Chair’s Initiative and this publication and volunteered time to take learning calls, speak at events, and offer clarifying and valuable policy insight. All of those who joined in the four convenings and spoke on panels and in roundtable discussions provided incredible perspectives to the Governors and advisors in the room and altogether made this Playbook possible. They are some of the brightest changemakers in youth mental health, and the NGA, Governor Murphy and the project team are incredibly grateful for their time and remain in admiration of their work.
- Accenture
- AHIP
- Amazon
- American Psychological Association
- Annie E. Casey Foundation
- Boston Consulting Group
- Biogen
- Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
- Children’s Hospital Association
- CVS Health
- Deloitte
- Elevance Health
- Effective School Solutions
- Everytown for Gun Safety
- Funders for Adolescent Science Translation
- Gilead
- Inseparable
- Johnson & Johnson
- Kaiser Permanente
- Kennedy Forum
- March of Dimes
- Maximus
- McKinsey
- Mental Health America
- Merck
- Meta
- Organon
- Penner Family Foundation
- Perigee Fund
- Pfizer
- Philips
- Pritzker Children’s Initiative
- Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
- Sanofi
- Walmart
- Western Governors University
- W.K. Kellogg Foundation
Project Team
- Timothy Blute, Director for the NGA Center for Best Practices
- Jordan Hynes, Director of the Children and Families program at the NGA Center for Best Practices
- Jessica Kirchner, Policy Analyst for the Children and Families program at the NGA Center for Best Practices
- Brianna Keys, Senior Policy Advisor, Office of New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy
- Laura Console, Senior Policy Advisor, Office of New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy
- Alex Hermann, Director of Federal Affairs, Office of New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy
- Colleen Desmond, Managing Director and Partner, Boston Consulting Group
- Dr. Jonathan Lim M.D., Managing Director and Partner, Boston Consulting Group
- Jessica Bester, Project Leader, Boston Consulting Group
Additional Resources
National Resources
- The AAKOMA Project: State of Mental Health of Youth of Color 2022
- The Trevor Project: 2022 National Survey on LGBTQ Youth Mental Health
- 2011-2021 Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 2021 Surgeon General Advisory on Protecting Youth Mental Health
- Hopeful Futures Campaign: America’s School Mental Health Report Card
- The National Academies: The Promise of Adolescence, Realizing Opportunity for all Youth
Prevention
- The Jed Foundation: The Comprehensive Approach to Mental Health Promotion and Suicide Prevention for High Schools
- Child Mind Institute: 2022 Children’s Mental Health Report – Treating Symptoms of Trauma in Children and Teenagers
- National Center for Children in Poverty: Medicaid Policies to Help Young Children Access Key Infant-Early Childhood Mental Health Services: Results from a 50-State Survey
- NGA: Resource Guide On State Actions To Prevent And Mitigate Adverse Childhood Experiences And Trauma
Stigma and Awareness
Workforce
- NGA: Help Wanted: Building A Pipeline To Address The Children’s Mental Health Provider Workforce Shortage
- Mental Health America: Youth and Young Adult Peer Support: Expanding Community-Driven Mental Health Resources
Supporting Educators and Caregivers
- Blue Cross Blue Shield: Understanding how youth mental health impacts your workforce
- Effective School Solutions: National Polling of Administrators & Parents on Mental Health Care in Schools
Strengthening Youth Mental Health: Training And Supporting Caregivers And Educators
In response to rising rates of mental health distress among young people, NGA Chair New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy introduced his NGA Chair’s Initiative last July. Through the Strengthening Youth Mental Health initiative, Governors from across the nation are collaborating to develop bipartisan solutions.
The fourth and final roundtable of the National Governors Association 2022-2023 Chair’s Initiative on Strengthening Youth Mental Health was held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on May 18, 2023. NGA Chair New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy and First Lady Tammy Murphy were joined by Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro and First Lady Lori Shapiro, Delaware Governor John Carney and state representatives from Louisiana, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Virginia. Conversation centered on the role states can play to enable and equip a wide range of caregivers and educators with training and tools to support youth mental health.
The roundtable opened with a conversation with Goldie Hawn, Academy Award winning actress and founder and CEO of the Hawn Foundation. The Hawn Foundation’s signature program, MindUP, aims to help children and their families better understand the brain science behind resiliency and develop tools to manage emotions and stress. Ms. Hawn spoke on the importance of teaching youth that they can have agency over their mental health and providing them the tools to do so.
State Policy Solutions Discussed At The Roundtable Include:
Educator And Community Training And Support
To expand youth support structures, Governors and state leaders can implement policies and programs to:
- Offer culturally competent trainings for a range of school staff and youth-facing adults on how to identify and respond to risk factors and warning signs of earlier mental health and substance use disorders
- Build awareness around available care and resources for youth facing adults
- Implement trauma-informed and culturally competent approaches within spaces like schools, after-school organizations, extra-curricular activities and sports teams
- Coordinate sustainable funding for school-based mental health supports, including leveraging federal funds, such as Medicaid
- Create evidence-based guidance and standards for the design and implementation of youth mental health services within schools, using multi-tiered systems of support (MTSS) as a framework
- Support educators’ ability to address their own mental health challenges and avoid burnout by investing in mental health resources and benefits for staff members
- Ensure faith leaders, out-of-school programs, sports coaches and other youth-facing adults have a voice in policymaking conversations
- Create relationships with and elevate the voices of “wellness champions” within faith-based and other communities
- Incorporate youth peer support models by creating youth peer support specialist certifications and adding-on youth and young adult training for current certified peer support specialists who support young people
- Grow the school mental health workforce by implementing licensing changes to target key shortages and introducing or expanding school mental health professional pipeline programs
Caring For The Caregivers
States can empower caregivers by:
- Dedicating funding for trusted, community-based organizations that offer parent and caregiver peer support programs
- Creating regional task forces to address workforce incentives and collaboration with community providers
- Upholding the testimony of caregivers and including their expertise and experiences in policymaking conversations
- Reducing administrative barriers within state systems to support whole-child and whole-family treatment approaches that include parental mental health care and peer supports
- Engaging youth in leadership positions, such as a Governor’s Commission or advisory boards that have authority to address issues important to youth and provide recommendations directly to the Governor and leaders in the agencies
- Maximizing regulatory flexibilities, available technology and licensing changes to enable tele-mental health care to lessen logistical burdens for families
- Developing a comprehensive system of care that offers wraparound supports for youth and families with complex needs and respite care to reduce caregiver burnout
- Explore including system navigation, peer supports and caregiver resources in Medicaid managed care contracts

Governors Lead Roundtable on Access and Affordability of Care
During a two-day roundtable event in Detroit, held April 19-20, 2023, Governor Murphy and Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer held discussions with First Spouses, private sector leaders, and policy and subject matter experts focused on the role of states in ensuring access and affordability of quality youth mental health treatment and care. New Jersey First Lady Tammy Murphy, North Carolina First Lady Kristin Cooper and North Dakota First Lady Kathryn Burgum spoke at the event, which also focused on expanding access and quality of care for maternal and infant health.
“Every single kid deserves to have their mental health supported. As governors, we’re committed to ensuring that the young people in our states – and every state – can access the mental health support they need to thrive.”
Governor Phil Murphy and Governor Gretchen Whitmer (Detroit News)
State Policy Solutions Discussed At The Roundtable Include:
Access And Affordability
- Conduct a fiscal mapping of the sources and allocation mechanisms of funding streams for youth mental health to understand gaps and opportunities for improvement
- Identify additional sources of funding, such as private and philanthropic funds, to support upstream community services that support prevention and resilience-building
- Develop innovative payment models and policies that allow for a greater integration of services among primary, pediatric, and behavioral health care providers, and drive high-quality, evidence-based, equitable outcomes for children
- Invest in integrated care and wraparound models such as coordinated specialty care for early psychosis
- Reevaluate Medicaid reimbursement rates compared to service costs for local providers
- Ensure compliance with the EPSDT mandate and expand preventative mental health services to all Medicaid-eligible students
- Identify solutions to provide patients with the right level of care for their needs, including digital tools and non-clinical support
- Appoint state insurance regulators to collect and review commercial insurance plans’ parity analyses and data reporting, including youth-specific parity compliance, to assess the equivalence of medical/surgical and mental health and substance use disorder coverage
- Continue post-pandemic support for telehealth and digital technology services, including supporting legislation and guidance, encouraging appropriate reimbursement, and exploring waivers for continuous enrollment and wraparound supports for youth and their families
- Leverage lived experience perspectives to help identify policies and regulations that create barriers to care for consumers, or unnecessary burdens for providers
- Explore care or compensation models for non-clinical professionals, like peer mentors and community health workers or home-visiting workers.
Workforce Development
- Explore incentivizing upskilling for primary health care providers and pediatricians on youth mental health, and formalize connections between these providers and psychiatrists and psychologists to enable advice-sharing and easier referrals
- Train early childhood professionals and school-based or community health workers to support prevention and screening activities, and manage the early signs of mental health challenges
- Increase high school and college student awareness of career paths in the youth mental health care workforce and pathways into these occupations, to develop a long-term pipeline of diverse talent
- Explore new or increased tuition subsidies and loan forgiveness programs for mental health professionals, potentially in exchange for work in specific communities or in private or public networks
- Promote a team-based and integrated approach to care in general medical education and by engaging multi-disciplinary providers to expand capacity of highly credentialed or severe-acuity providers, like psychiatrists
- Review licensing and scope of practice regulations requirements for mental health professionals to maximize the ability of mental health professional to work to their license, while maintaining education and training standards that align with high-quality care
- Examine telehealth and cross-state state licensing flexibility and agreements, including multi-state compacts, as a means of supplementing pediatric network capacity and maximizing the scope of practice for providers across states
- Eliminate culturally or otherwise outdated questions from the licensing testing process that could discourage potential applicants
- Bolster administrative support for under-staffed licensing offices and modernize application processes
- Encourage the composition of licensing boards to reflect demographics, and comprise multiple areas of expertise required in a team-based approach to youth mental health
System Alignment And Innovation
- Meet children and adolescents where they are through the provision and reimbursement of mental health services in schools, community locations, and primary care settings
- Compel and formalize collaboration to reduce silos between youth-focused government agencies that oversee mental health and other services to address the social determinants of health, such as food security and housing
- Convene community stakeholders–including providers, payers, caregivers and others along the care continuum–to discuss challenges and to promote collaboration
- Map capacity standards across youth mental health patient journeys to understand supply, demand, and gaps
- Enable data sharing amongst youth-facing state agencies, including law enforcement, to ensure accurate and up-to-date information can be employed to treat individuals’ mental health challenges
- Identify the different points of entry into the system, and develop infrastructure to ensure there is “no wrong door” to accessing help
- Invest in upstream prevention and intervention, including addressing social factors and services to reduce pressure on downstream crisis services and in-patient capacity
- Integrate youth-specific crisis response services (including services accessed through 988, mobile crisis, crisis receiving and stabilization, community programming, warm lines, peer supports) into the broader youth mental health landscape, to enable connection to the continuum of care
2023 NGA Winter Meeting
NGA Chair New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy opened the the 2023 NGA Winter Meeting with a plenary session on Strengthening Youth Mental Health. In response to rising rates of mental health distress among young people, Governor Murphy first introduced his NGA Chair’s Initiative in July of 2022. Through the Strengthening Youth Mental Health initiative, Governors from across the nation are collaborating to develop bipartisan, state solutions. Governor Murphy and Utah Governor Spencer Cox provided opening remarks before turning the discussion over to moderator Dr. Alfiee Breland-Noble, Founder, The AAKOMA Project.
The panel, consisting of Governor Murphy, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, Dr. Richard Besser, CEO, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Reina Chiang, a college student and founder of the nonprofit, “u matter apparel,” and First Lady Tammy Murphy discussed elevating and expanding the national conversation around youth mental health and the close link between youth mental health and maternal and infant health. Watch the full session.
“As leaders, one of the most important and sacred responsibilities is protecting the health and well-being of our kids, and for far too long, mental health and well-being of our young people has been overlooked, and the consequences are impossible to miss. From small towns to big cities, America’s youth mental health crisis is playing out in homes, schools, hospitals and beyond.”
Governor Phil Murphy

Governor Murphy and Governor Polis Join Forces To Tackle Youth Mental Health Crisis
The second roundtable of the 2022-2023 NGA Chair’s Initiative: Strengthening Youth Mental Health was held on January 24-25, 2023, in Santa Monica, California. During the two-day roundtable, NGA Chair New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy and Colorado Governor Jared Polis held discussions with parents, physicians, pediatric psychologists, educators, policymakers and other mental health experts. Over the two days, roundtable discussions unpacked the Initiative’s second pillar focusing on themes of building a foundation of diversity and equity in addressing stigma, reducing the stigma of mental health and seeking help, and increasing awareness around youth mental health.
Compared to previous generations, young people today are much more open to talking about mental health and want to play an active role in reducing the stigma surrounding mental health challenges to promote mental wellbeing. Throughout the convening, the young leaders in attendance shared impassioned stories of both their own mental health struggles and the many ways in which youth are organizing to break the stigma. Despite this progress, stigma continues to be a major barrier to young people reaching out for help. Although half of mental health disorders begin by age 14, treatment is often delayed by a decade or more as youth and their families grapple with feelings of fear and shame. Stigma is a reality across different settings: cultural disconnects or generational divides within the home can make it difficult to talk about mental health, and misconceptions continue to pervade attitudes in educational settings, places of worship, and workplaces. Bias, conscious or unconscious, within the healthcare system, can also have a stigmatizing effect on those who need respect, understanding, and support from providers.

Solutions To Break The Stigma And Support The Conversation Around Mental Health
Governors can increase awareness and reduce stigma by supporting:
- Existing community-based mental health organizations’ awareness-building efforts: Ensuring funding and other resources get to organizations with deep knowledge of their communities’ mental health challenges
- Targeted anti-stigma campaigns with a focus on storytelling: Developing efforts driven and co-designed by young people, that reach young people on social media, and are focused on diverse populations, including youth of color and Indigenous youth, LGBTQIA+ youth, youth involved in the foster care system, etc. Governors can also humanize mental health by using their platforms to share their personal journeys with mental health
- School mental health curriculums: Growing capacity for mental health literacy for youth and their families by implementing age-appropriate awareness of the spectrum of mental health, bolster mental wellbeing, and encourage youth to seek help, as well as adopting family engagement plans and public-private partnerships to tap into the knowledge and support of thought leaders in the private or nonprofit sector
- Suicide stigma reduction: Normalizing discussing suicide and suicidal ideation, making them less “scary” and unbroachable topics by training youth peers, as well as the adults who live and work with youth, on appropriate and compassionate responses to someone who is experiencing intrusive thoughts can help to reduce the silence around suicide
- Sensitivity training for adults interacting with youth: Enabling sufficient support, care, and treatment for youth experiencing mental health challenges through bias, sensitivity, and cultural responsiveness training for healthcare professionals, educators, and others
- The power of peer networks: Recognizing a recent Active Minds survey that found that 67% of young adults first tell a friend they are feeling suicidal before telling anyone else – supporting the development of a diverse mental health workforce of peer supporters and community health workers to complement a workforce that is able to provide culturally competent care when and where families need it at the level that is needed; including through trainings on mental health identification and crisis management
- Crisis services that meet youth where they are: Protecting young people’s privacy and enabling trust through innovative services such as anonymous text lines or apps and in building youth-specific crisis response systems including home-crisis models
- Delivery systems improvements to promote trust and safety: Addressing the experience patients have when they seek care after breaking the stigma of seeking help, including addressing the trust gap between patients and the health care system
- Increased awareness of people working in programs that support the well-being needs of youth: increasing awareness of youth mental health among all state systems and agencies that touch the lives of youth and their families, including public health staff, human services staff, youth employment systems, out of school time staff, justice, or housing and child welfare systems
- Safe and supportive school environments: Implementing mental health awareness and stigma-reducing tools in schools such as anti-bullying measures and adding information on seeking mental health (988) to student IDs, utilizing yearly school climate improvements surveys to understand current youth needs; incorporating trained peers into campus programming; and considering alternatives to exclusionary discipline
governors and states meet on prevention and resilience in youth mental health
On October 18-19, 2022, in Salt Lake City, Utah, National Governors Association (NGA) Chair New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy and NGA Vice Chair Utah Governor Spencer Cox held the first of four roundtables to discuss the 2022-2023 NGA Chair’s Initiative: Strengthening Youth Mental Health. A strong state contingent was represented, including Alabama, Arkansas, Minnesota, New Mexico, and Pennsylvania. States were joined by over fifty community leaders, academic experts, and representatives from partner organizations and funders.
The convening centered on practical solutions for the first of the initiative’s four pillars: prevention and resilience building. Discussions forged connections across the public and private sectors, shared best practices across states and territories to amplify their impact, and aligned on ways that Governors can further support youth mental health.
Key themes on prevention and resilience were unpacked across three discussions that centered the voices of those with first-hand experience of youth mental health from different perspectives; focused on applying the brain and behavioral science of resiliency, specifically to provide opportunities to build and rebuild mental health in youth; and oriented the group towards practical and implementable solutions. Credentials spanning academia, government, business, and community service were interwoven with personal stories of delegates’ lived experience.
Despite the immense challenge, the roundtable discussion coalesced around hope: evidence shows that prevention and resilience building in childhood and adolescence can fundamentally change the trajectory of a child and family’s life. Given supportive environments and the right skillset, the effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and exposure to toxic stress can be successfully managed to prevent mental health challenges from developing or worsening. Strengthening youth mental health, starting with prevention and a focus on resilience, needs to be a key priority within all levels of government, and across all sectors of society.
About the Initiative

Governor Phil Murphy’s 2022-2023 Chair’s Initiative is focused on four key pillars to address youth mental health:
Addressing Prevention and Resilience Building
Providing youth with the supports and tools necessary to cope with stressors and challenges, helping them to thrive and reduce likelihood of engaging in unhealthy or damaging behaviors.
Increasing Awareness and Reducing Stigma
Promoting awareness of mental health resources and foundational mental health knowledge by expanding easy access points to education, helplines and state services.
Insuring Access and Affordability of Quality Treatment and Care
Addressing the barriers that prevent youth from accessing care including ensuring high quality care is available in the places, spaces, and timeframes that youth want and need, and that costs and lack of insurance coverage do not prevent access.
Training and Supporting Caregivers and Teachers
Examining not just the core issues around youth mental health, but also considering the impacts of youth mental health challenges, including the tie-in to academic recovery.
Expanding existing training and supports so that those caring for and interacting with youth daily have the tools and understanding to identify mental health needs and how to facilitate access to supports for youth
Improving Maternal and Infant Health
In addition, First Lady Tammy Murphy is leading an effort focused on maternal and infant health (MIH). This has been a significant area of focus in New Jersey throughout the Murphy Administration and this effort seeks to elevate and expand the conversation around maternal and infant health nationwide.

The four pillars of this effort are:
- Centering Women’s Voices in MIH Policy – This area focuses on the importance of integrating the voices of mothers and women of color in the policymaking process, making sure they have a seat at the table before the table is even built.
- Improving and Utilizing Maternal and Infant Health Data – Improving data systems by incorporating qualitative data on maternal health experiences, linking state data and increasing accessibility to data to improve accountability.
- Expanding Access and Quality of Care – Identifying ways for states to ensure citizens have access to high quality maternal and infant care, including various MIH Medicaid policies that states can look to implement.
- Elevating Innovative MIH Polices, Programs and Technologies – Identify and highlight innovative and novel approaches to MIH policy, including highlighting effective programs and examining the role of technology to improve MIH outcomes.
2022 Summer Meeting
Insights – Youth Mental Health & Maternal and Infant Health
NGA has collated a variety of resources from stakeholders to assist Governors and their staff with strengthening youth mental health, and improving maternal and infant health. These resources leverage the expertise of NGA partners to provide insights to assist with delivering specific program areas and cross-program tools and best practices.

Shifting Upstream: State Actions to Support School-Based Mental Health Screening
Addressing the US’s youth mental health crisis requires us to screen more children for relevant conditions to enable appropriate intervention earlier. Universal screening can be advanced by meeting kids where they are: in schools.

America’s School Mental Health Report Card
School mental health services play an important role in supporting youth and helping every child thrive. This report highlights what each state is doing to support school mental health services and provides policy recommendations and examples of policy pacesetters from across the country.

Supporting Adolescent Health and Development
A brief highlighting the specific findings on youth behavioral health from two National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine reports: The Promise Of Adolescence: Realizing Opportunity For All Youth and Promoting Positive Adolescent Health Behaviors And Outcomes: Thriving In The 21st Century.

Addressing Maternal Health Disparities: Doula Access in Medicaid
This report discusses how women using doulas in Medicaid have fewer inpatient hospital admissions during pregnancy, are more likely to attend their postnatal visit, experience lower odds of cesarean delivery, have lower odds of postpartum depression or anxiety, and have lower overall costs compared to women not using doulas.
Supporters
-
Accenture

-
AHIP

-
Amazon

-
Annie E. Casey Foundation

-
BCG

-
Biogen

-
Blue Cross Blue Shield

-
Children’s Hospital Association

-
CVS

-
Deloitte

-
Elevance Health

-
Effective School Solutions

-
Everytown for Gun Safety

-

Funders for Adolescent Science Translation
-
Gilead

-
inseparable

-
Johnson & Johnson

-
Kaiser

-
Kennedy Forum

-
March of Dimes

-
Maximus

-
McKinsey
-
Merck

-
Meta

-
Organon

-

Penner Family Foundation
-
Perigee Fund

-
Pfizer

-
Philips

-
Pritzker Children’s Initiative

-
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation

-
Sanofi

-
Walmart

-
Western Governors University

-
W.K. Kellogg Foundation



